Quelea’s programming model encourages programmers to define operations on a replicated data object as folds over effects accumulated over the object. A straightforward implementation, which lets effects to simply accumulate over time would not scale. Quelea implements effect summarization (or, garbage collection), which is the key to ensure that the programming model remains practical and competitive to alternative models. The aim of this benchmark is to facilitate experiments to demonstrate the impact of garbage collection. We use Last-Writer-Wins register operations for this purpose.
Building the benchmark
Navigate to ~/git/Codeec/tests/LWW and run make LWW_1key. It
produces one binary named LWW_1key.
Running the benchmark
LWW_1key implements three garbage collection policies - No_GC,
GC_Mem_Only, and GC_Full, each corresponding to a different curve
on Fig. 9(d) of the paper. We conduct three
experiments with the binary, each lasting for 1 minute and employing
different garbage collection strategy. For 1 minute, clients keep
making write and read requests (with an inter-request delay of 1ms
(1000 μs)) to a single LWW register object. For each GC strategy, we
then measure how many client requests have been served under 1 minute.
No GC
Corresponds to Quelea with no effect summarization. The command to run is:
./LWW_1key --kind Daemon --numRounds 10000 --numThreads 2 --measureLatency --gcSetting No_GC --terminateAfter 60
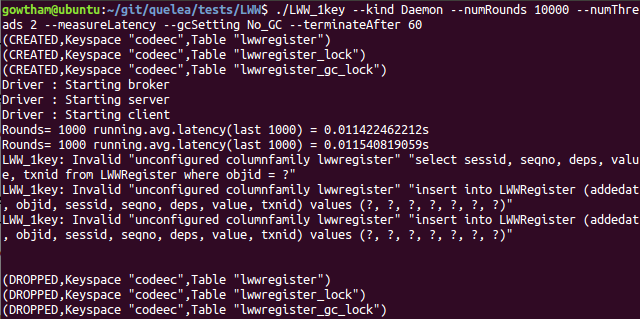
Ignore the Unconfigured column family errors, if any; these are
generated by outstanding requests after 60s timout has been reached,
and Cassandra column families have been dropped. However, if there are
any ZMQError messages, please refer to the troubleshooting guide
for a quick fix.
GC in memory only
This is the case where Quelea does garbage collection only in the memory, but not on the disk. The command to run is:
./LWW_1key --kind Daemon --numRounds 10000 --numThreads 2 --measureLatency --gcSetting GC_Mem_Only --terminateAfter 60
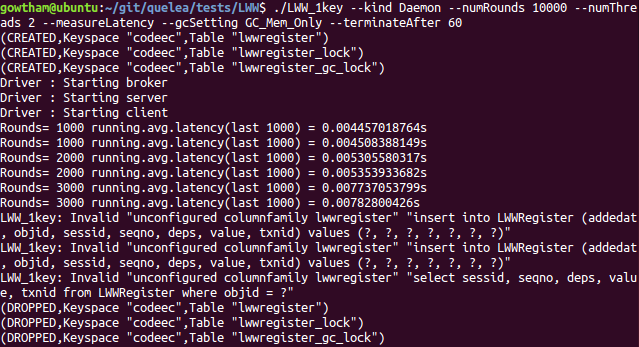
Full GC
Corresponds to Quelea with effect summarization in both memory and disk. The command to run is:
./LWW_1key --kind Daemon --numRounds 10000 --numThreads 2 --measureLatency --gcSetting GC_Full --terminateAfter 60
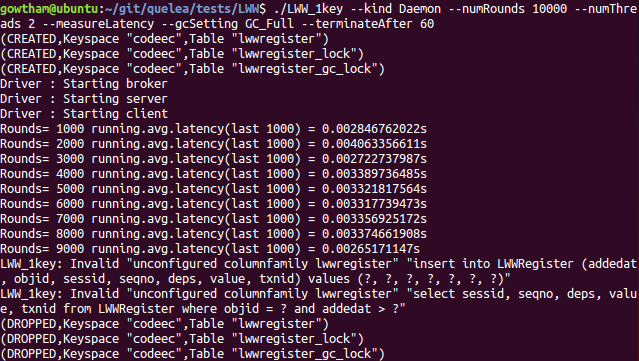
Observations
As sample runs demonstrate, you should be able to observe that Quelea with effect summarization is orders of magnitude more scalable than one without.